- What is investment
- money spent or expenditures on
- new parts ( factories )
- Capital equipment ( Machinery )
- Technology ( hardware and software )
- New homes
- Inventories
- Expected rate of return
- How does business make investment decisions
- cost/ benefit analysis
- How does business determine the benefit
- expected rate of return
- How does business count the cost
- Interest costs
- How does business determine the amount of investment they undertake
- How do you compute the real interest rate (r%) - r% = i% - 𝚷% ( real GDP = Nominal GDP -Inflation)
- What then, determines the cost of an investment
- What is the slope of the investment demand curve
- Downward Sloping
- Why
- when interest rates are high, fewer investment are profitable; when interest rates are low, more investment
- Shift in investment demand
- Cost of production
- Business taxes
- Technological
- Stock of capital
- Expectations
- Aggregate Supply- The level of real GDP (GDPr) that firms will produce at each price level
- Long- Run Vs. Short- Run
- Long Run- Period of time where input prices are completly flexible and adjust to changes in price level
- The long run, the level of real GDP supplied is independent of the price level
- Short Run- period of time where input prices are sticky and do not adjust to changes in the price level
- In the short run, the level of real GDP supplied is directly related to the price level
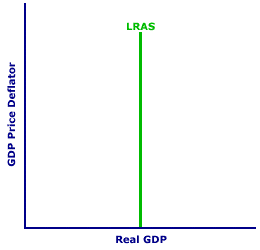
- Long- Run Aggregate Supply (LRAS)
- The long- run aggregate supply or LRAS marks the level of full employment in the economy
- Short-Run Aggregate supply (SRAS)
- Because input prices are sticky in the short-Run, the SRAS is upward sloping
- Changes in SRAS
- An increase in SRAS is seen as a shift to the right
- A decrease in SRAS is seen as a shift to the left
- The key to understanding shift in SRAS is per unit cost of production
- Per unit production cost = Total input / Total output cost
- Determinants of SRAS
- input prices
- productivity
- Institutional Environment
- input rices - domestic resource rate
- wages ( 75% of all business costs )
- Cost of capital
- Raw materials ( Commodity prices )
- foreign resource prices
- strong money = lower foreign prices
- Weak money = Higher foreign resource prices
- Market power
- monopolies and cartels that control resources control the prices of the resources
- increase in resource prices = SRAS shift right
- Decrease in resource prices = SRAS shift left
- More productivity = lower units production cost = SRAS shift left
- Lower productivity = higher unit production cost = SRAS shift right
- legal- institutional environment
- taxes and subsides
- taxes ( money to government ) on business increase per unit production cost = SRAS shift left
- Subsides ( money from government ) to business reduced per unit production cost = SRAS shift right
- Government Regulation
- Government regulation creates a set of compliance = SRAS shift left
- Deregulation reduces compliance cost = SRAS shift right
Tuesday, March 7, 2017
Unit 3 February 21
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)


No comments:
Post a Comment