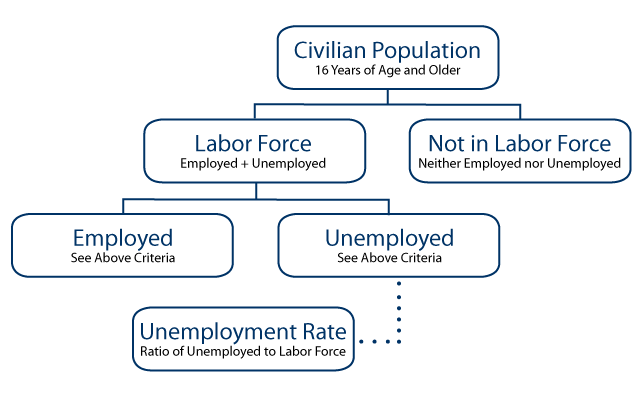
- Unemployment- the percentage of people who don't have jobs that are in the labor force
- Unemployment rate = #unemployment ➗#in labor force ✖ 100
- labor fore = Unemployment = employment
- standard unemployment is 4-5%
- people not in the labor force
- kids
- military personal
- people in mental institutions
- home makers
- retired people
- full-time students
- people in jail or prison
- discouraged
- 4 types of unemployment
- Frictional Unemployment
- "Temporarily Unemployment" or being between jobs
- individuals are qualified workers with transferable skills but they aren't working
- Seasonal Unemployment
- this is a specific type of frictional unemployment which si due to time of year and the nature of the job
- these jobs will come back
- Structural Unemployment
- Change in the structure of the labor force make some skills obsolete
- Workers don't have transferable skills
- Cyclical Unemployment
- as demand for goods and services falls, demand for labor falls and workers are fired
- The natural rate and fall employment
- two of the three types of unemployment are unavailable
- frictional
- structural
- Together they make up the natural rate of unemployment
- frictional + Structural = NRU (4-5%)
- full employment means no cyclical unemployment
- okun's law- when unemployment rises 1% above the natural rate, GDP fall by 2%
- People that are employed
- Part time workers
- people on a leave of absence
- people who work 1 hour a month
Monday, February 13, 2017
Unit 2- February 9
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
I thought it was very intelligent of how you worded your blog it definitely is clear and easy to understand. However I wish that you could've included examples or scenarios when you explained the 4 types of unemployment to help me better comprehend. The chart was a very. I've touch it is a great visual representation.
ReplyDeleteI thought your blog was very hslpeful and detailed. I liked how your notes were sectioned off so they were very neat and easy to understand. However I did wish that you had given examples for the 4 types of unemployment in order to create a better understanding between the different types.
ReplyDelete