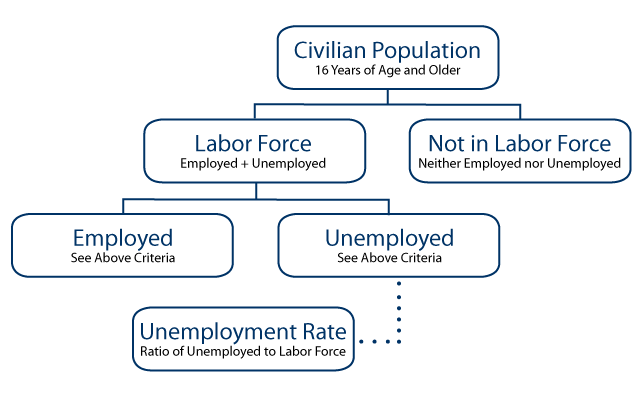
- Unemployment- the percentage of people who don't have jobs that are in the labor force
- Unemployment rate = #unemployment ➗#in labor force ✖ 100
- labor fore = Unemployment = employment
- standard unemployment is 4-5%
- people not in the labor force
- kids
- military personal
- people in mental institutions
- home makers
- retired people
- full-time students
- people in jail or prison
- discouraged
- 4 types of unemployment
- Frictional Unemployment
- "Temporarily Unemployment" or being between jobs
- individuals are qualified workers with transferable skills but they aren't working
- Seasonal Unemployment
- this is a specific type of frictional unemployment which si due to time of year and the nature of the job
- these jobs will come back
- Structural Unemployment
- Change in the structure of the labor force make some skills obsolete
- Workers don't have transferable skills
- Cyclical Unemployment
- as demand for goods and services falls, demand for labor falls and workers are fired
- The natural rate and fall employment
- two of the three types of unemployment are unavailable
- frictional
- structural
- Together they make up the natural rate of unemployment
- frictional + Structural = NRU (4-5%)
- full employment means no cyclical unemployment
- okun's law- when unemployment rises 1% above the natural rate, GDP fall by 2%
- People that are employed
- Part time workers
- people on a leave of absence
- people who work 1 hour a month
Monday, February 13, 2017
Unit 2- February 9
Unit 2- February 2
- Inflation- an increase or rise in price
- Purchasing power- the amount of goods and services that your money can buy
- three causes of inflation
- printing too much money
- demand-pull inflation
- it is caused by and excess of demand over output that pulls prices upward
- cost-push inflation- it is caused by a rise in per unit production cost due to increasing resources cost
- inflation rate formula- current year price index - base year price index ➗ base year price index ✖ 100
- Rule of 70- it is used to calculate the number of years it will take for the price level to double at any given rate of inflation
- 70 ➗ annual rate of inflation
- the ideal inflation rate should be 2-3%
- Deflation- a general decline in price level
- Disinflation- occurs when the inflation rate declines
- Nominal interest rate- the unadjusted cost of borrowing a lending money
- Real interest rate- the cost of borrowing or tending, adjust for inflation
- Nominal - Expected inflation
- Hurt by inflation
- lenders-people who lend money (at a fixed interest rate )
- People with fixed income
- Savers
- Helped by inflation
- Borrowers- people who borrow money
- a buisness where the price of the product increases faster than the price of resources
Sunday, February 12, 2017
Unit 2- February 3
- Nominal GDP- the value of output produced in current prices
- it can increase from year to year if either output or prize increases
- Real GDP- the value of output on constant base year prices
- it adjust for inflation
- it only increases if output increases
- formula is P * Q
- use real GDP to measure economic growth
- in the base year real GDP and Nominal GDP are equal
- in years after the base year nominal GDP will exced real GDP
- in years before the base year, real GDP will exceed nominal GDP
- GDP Deflator- a price index used to adjust from nominal to real GDP
- nominal GDP ➗ Real GDP ✕ 100
- in the base year GDP Deflator will always equal 100
- for years after the base year GDP deflator is greater than 100
- for years before the base year GDP deflator is less than 100
- Consumer price index( CPI )- it measures inflation by tracking changes in the price of a markets basket of goods
- Price of market basket in the current year ➗Price of market basket in the base year ✕ 100
Unit 2- January 31
- Expenditure approach to GDP
- expenditure is spending
- Income approach to GDP
- Wager rents interest profits + Statistical Adjustments
- Trade = Exports - Imports
- Budgets= government purchases of goods and services + government transfer payment - government tax and fee collection
- if the number is positive its a deficit, if its negative its a surplus
Unit 2- January 30
- GDP- Gross Domestic Product
- The total value of all final goods and services produced within a country's borders within a giving year
- GNP- Gross national product
- The total value of all final goods and services produced by americans in a given year.
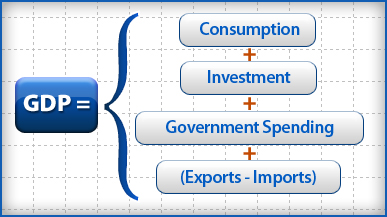
- GDP= C + Ig + Xn
- C- Consumption ( Includes the purchases of final goods and services)( 67% of economy)
- Ig-Gross Private Domestic Investment (18% of the economy) (Includes new factor equipment, factory equipment maintenance, construction of housing, unsold inventory of product build in a year)
- G- Government spending (17% of the economy) ( government purchasing goods and services)
- Xn- Net exports (exports - imports) ( -2% of the economy)
- Included in GDP
- C, Ig, G, Xn
- Excluded in GDP
- Intermediate goods
- adding double or multiple country
- Second hand goods
- avoiding double or multiple counting
- Stock and Bonds
- no production involved
Unit 2- January 26
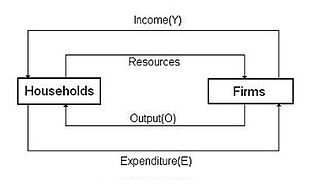
- Circular flow model- it represents the trade of an economy by flows around the circle
- Household- a person or group of people who share an income
- Firm- An organization that produces goods and services for sale
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)